Dr Debabrata Dash, MD (Medicine), DM (Cardiology), FICC, FCCP, FAPSC, FSCAI, FACC, FSCAI, FESC, FACC is a consultant interventional cardiologist at Aster Hospital, Dubai. Earlier in his career, he worked at Veterans General Hospital (Taipei, Taiwan), Toyohashi Heart Center (Toyohashi, Japan) and Guangdong Provincial Hospital (Guangzhou, China). He set up the interventional cardiology department and worked as a Director of Cath Lab and Consultant Interventional Cardiologist in S.L Raheja (A Fortis Associate) hospital (Mumbai, India) and Sai Bhavani Super Specialty Hospital (Hyderabad, India). He has accumulated vast experience of over 20 years in interventional cardiology. He had served as a vice chairperson of interventional cardiology in the Asia Pacific region for 2 years. He represented India as invited as international faculty in China, Korea, Japan, Latin America, Vietnam, USA, Malaysia, & Singapore to present the latest developments in interventional cardiology.
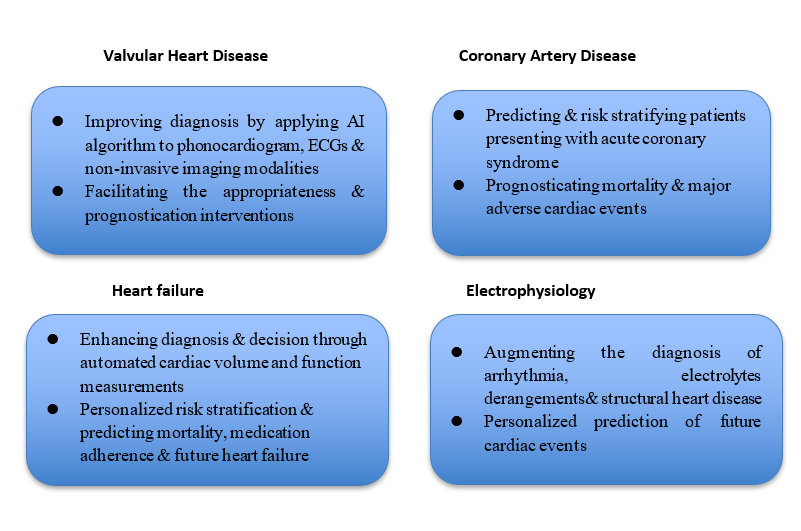
Artificial intelligence (AI) has brought forth a new era of possibilities in the ever-changing healthcare scene, with a considerable impact on cardiovascular illnesses. AI has progressed from experimental uses to becoming a key instrument in changing the face of cardiovascular health in recent years. There is a growing appreciation for the role of AI in helping guide clinicians manage patients with heart failure (HF). AI algorithms have been developed and validated for risk stratification and predicting mortality, medication adherence and recurrent hospitalizations in patients with HF.
AI can detect hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a genetic disorder that occurs when the walls of the heart muscle thicken, resulting in the heart’s reduced ability to pump out and take in blood.
Cardiac arrhythmias refer to abnormal atrial or ventricular rhythms and are estimated to affect 1.5–5% of the general population, with atrial fibrillation being the most prevalent arrhythmia in an ageing population. ECGs remain a key diagnostic tool for the timely diagnosis and management of arrhythmias. When applied to the ECGs AI is able to garner new insights with respect to diagnosis, risk stratification and prediction. AI improves clinical diagnosis by applying algorithms to phonocardiogram, ECGs, echocardiography and MRI. It facilitates the appropriateness and prognostication of interventions.
Medical learning (ML) algorithms play a significant role in the risk stratification, diagnosis, prognostication and management of patients with coronary artery disease, the most common type of heart disease responsible for highest mortality. A broad range of AI applications revolve around enhancing diagnostic capabilities and clinical decision-making through automated cardiac function measurements and AI-based predictive modeling.
AI has transformed medical imaging, offering previously unheard-of precision in the analysis of cardiovascular disorders, as a result of technological developments. Modern algorithms can now carefully examine MRI and CT scans, providing medical practitioners with a quick and precise diagnosis and characterization of anomalies in the heart and blood vessels. AI in medical imaging has greatly increased diagnostic capabilities, leading to more efficient treatment plans and better patient outcomes. The combination of AI and medical imaging has sped up the diagnosis process while simultaneously increasing diagnosis accuracy. Large databases of imaging data can be analyzed by AI algorithms, which can then swiftly spot patterns and abnormalities that human observers might miss. With the help of large patient datasets, ML algorithms can predict the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. This method allows for early intervention as well as the creation of individualized treatment programs based on the unique characteristics of each patient. Beyond conventional risk indicators, AI has predictive power in the assessment of cardiovascular risk. To provide more precise and unique risk assessments, machine learning algorithms can examine a wide variety of data, such as genetic data, lifestyle variables, and real-time health monitoring. This degree of accuracy enables medical professionals to carry out interventions and preventative measures that are customized to meet the unique requirements of every patient.
AI has become a vital tool in giving decision support to healthcare workers in the complex environment of cardiovascular care. AI-powered decision support systems integrate and analyze massive datasets, allowing clinicians to make informed and timely judgments. This collaborative approach strives to improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery by optimizing treatment regimens.
AI application in decision support systems extends beyond data analysis. Machine learning algorithms may learn and adapt on the fly in response to new information and emerging trends, giving healthcare professionals dynamic insights. This adaptive intelligence improves decision-making, especially when the volume and complexity of data overwhelm traditional methodologies.
AI has played a critical role in transforming the landscape of cardiovascular disease medication discovery. AI algorithms drive computational models that simulate the impact of numerous substances on the cardiovascular system. This not only speeds up the drug development pipeline, but it also promotes the rise of personalized medicine approaches, which customize therapies to specific patients’ unique genetic and physiological traits.
Traditional drug development techniques can be time-consuming and expensive. With the incorporation of AI in this field, computer models that can rapidly analyze huge datasets, forecast prospective medication candidates, and simulate their effects on cardiovascular health have been introduced. This speeding up of the drug development process has the potential to bring novel and more effective therapies to patients in a shorter period of time.
Significant progress has been made in the integration of AI with telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, which has led to a paradigm shift in the way cardiovascular care is provided. Patients with cardiovascular diseases can have round-the-clock monitoring thanks to wearables with sensors and AI algorithms. By enabling early anomaly detection, this real-time monitoring improves patient care by treating and preventing cardiovascular events pro-actively.
Patients with cardiovascular problems are now being tracked remotely in real-time instead of only once a month through periodic check-ins. Vital signs, including blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and heart rate, can be tracked by wearable technology, giving a complete picture of a patient’s cardiovascular health. The use of AI in cardiovascular medicine is anticipated to grow as technology develops, pushing the limits of what is practical for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. The continued development of AI applications holds the potential to completely transform cardiovascular care by offering patients everywhere more individualized, effective, and efficient treatments.